Add high-performance video to your Remix.js application
Use our API and components to handle embedding, storing, and streaming video in your Remix.js application
When should you use Mux with Remix.js?
When adding video to your Remix.js app, you'll encounter some common hurdles. First, videos are large. Storing them in your public directory can lead to excessive bandwidth consumption and poor Git repository performance. Next, it's important to compress and optimize your videos for the web. Then, as network conditions change, you might want to adapt the quality of your video to ensure a smooth playback experience for your users. Finally, you may want to integrate additional features like captions, thumbnails, and analytics.
You might consider using Mux's APIs and components to handle these challenges, and more.
Quickly drop in a video with Mux Player
The quickest way to add a video to your site is with Mux Player. Here's what Mux Player looks like in action:
import MuxPlayer from "@mux/mux-player-react";
export default function Page() {
return (
<MuxPlayer
playbackId="jwmIE4m9De02B8TLpBHxOHX7ywGnjWxYQxork1Jn5ffE"
metadata={{
video_title: "Test video title",
viewer_user_id: "user-id-007",
}}
/>
);
}If your site has just a few videos, you might upload them to Mux directly through the dashboard. In the Mux Dashboard, on your video assets page, select "Create New Asset". On the next screen, you can upload a video directly to Mux.
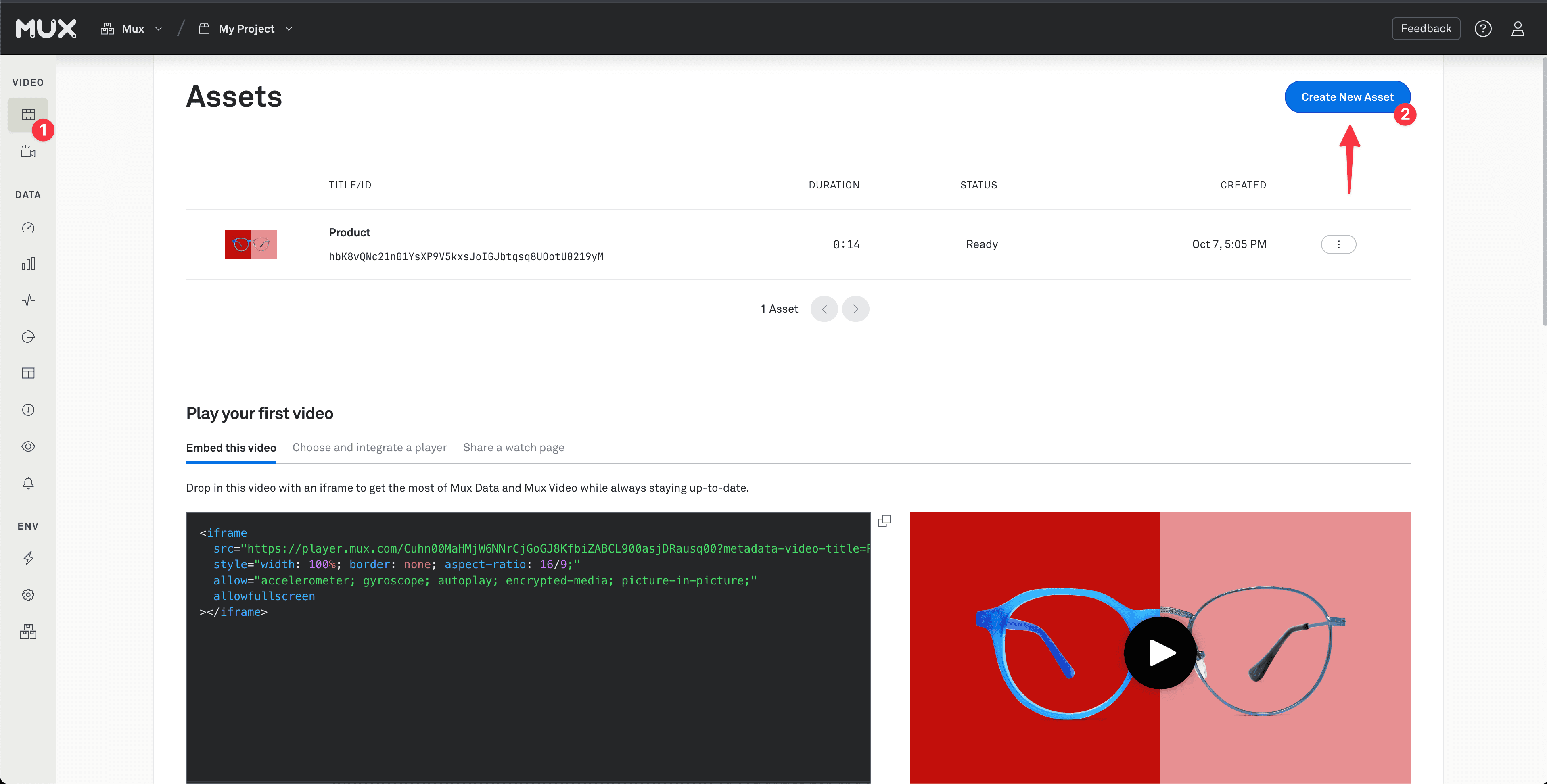
You'll then be able to see your new asset on your video assets page. When you click on the asset, you can find the asset's playback ID in the "Playback and Thumbnails" tab. This playback ID can be used in the playbackId prop of the Mux Player component.
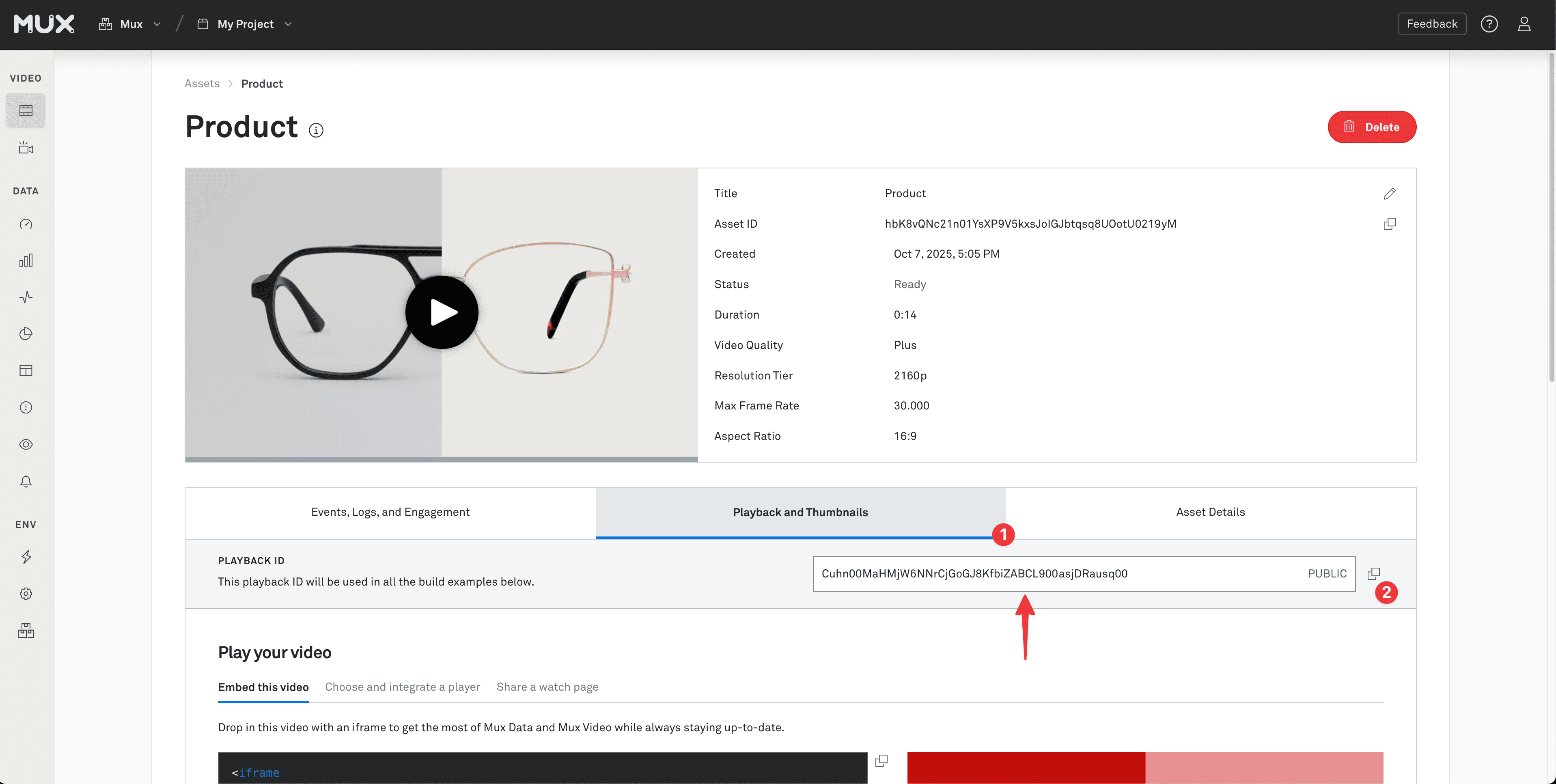
You can read more about Mux Player, including how to customize its look and feel, over in the Mux Player guides.
If you're managing more videos, you might take a look at our CMS integrations.
Finally, if you need more control over your video workflow, read on.
Use the API to build your video workflow
If you're looking to build your own video workflow that enables uploading, playback, and more in your application, you can use the Mux API and components like Mux Player and Mux Uploader.
Example: allowing users to upload video to your app
One reason you might want to build your own video workflow is when you want to allow users to upload video to your app.
Let's start by adding a new page where users can upload videos. This will involve using the Mux Uploader component, which will upload videos to a Mux Direct Uploads URLAPI.
In the code sample below, we'll create an upload URL using the Mux Node SDK and the Direct Uploads URL API. We'll pass that URL to the Mux Uploader component, which will handle uploading for us.
import { json } from "@remix-run/node";
import { useLoaderData } from "@remix-run/react";
import MuxUploader from "@mux/mux-uploader-react";
import mux from "~/lib/mux.server";
export const loader = async () => {
const upload = await mux.video.uploads.create({
new_asset_settings: {
playback_policy: ["public"],
video_quality: "basic",
},
cors_origin: "*",
});
return json({ url: upload.url });
};
export default function UploadPage() {
const { url } = useLoaderData();
return <MuxUploader endpoint={url} />
}In production, you'll want to apply additional security measures to your upload URL. Consider protecting the route with authentication to prevent unauthorized users from uploading videos. Also, use cors_origin and consider playback_policy to further restrict where uploads can be performed and who can view uploaded videos.
Next, we'll create an API endpoint that will listen for Mux webhooks. When we receive the notification that the video has finished uploading and is ready for playback, we'll add the video's metadata to our database.
import { json } from "@remix-run/node";
import Mux from "@mux/mux-node";
// this reads your MUX_TOKEN_ID and MUX_TOKEN_SECRET
// from your environment variables
// https://dashboard.mux.com/settings/access-tokens
const mux = new Mux();
// Mux webhooks POST, so let's use an action
export const action = async ({ request }) => {
if (request.method !== "POST") {
return new Response("Method not allowed", { status: 405 });
}
const body = await request.text();
// mux.webhooks.unwrap will validate that the given payload was sent by Mux and parse the payload.
// It will also provide type-safe access to the payload.
// Generate MUX_WEBHOOK_SIGNING_SECRET in the Mux dashboard
// https://dashboard.mux.com/settings/webhooks
const event = mux.webhooks.unwrap(
body,
request.headers,
process.env.MUX_WEBHOOK_SIGNING_SECRET
);
// you can also unwrap the payload yourself:
// const event = await request.json();
switch (event.type) {
case "video.upload.asset_created":
// we might use this to know that an upload has been completed
// and we can save its assetId to our database
break;
case "video.asset.ready":
// we might use this to know that a video has been encoded
// and we can save its playbackId to our database
break;
// there are many more Mux webhook events
// check them out at https://www.mux.com/docs/webhook-reference
default:
break;
}
return json({ message: "ok" });
};Finally, let's make a playback page. We retrieve the video metadata from our database, and play it by passing its playbackId to Mux Player:
import MuxPlayer from "@mux/mux-player-react";
import { useLoaderData, useParams } from "@remix-run/react";
export const loader = async ({ params, request }) => {
const { title } = getAssetFromDatabase(params);
const userId = getUser(request);
return json({ title, userId });
};
export default function Page() {
const { title, userId } = useLoaderData();
const { playbackId } = useParams();
return (
<MuxPlayer
playbackId={playbackId}
metadata={{
video_title: title,
viewer_user_id: userId
}}
/>
);
}And we've got upload and playback. Nice!
What's next? You can integrate with your CMS. You can optimize your loading experience. Or get started with the example project below:
Example projects
remix-examples/mux-video
This is a bare-bones starter application with Remix.js that uses:
- Mux Direct UploadsAPI and Mux Uploader
- Mux Video + Mux Data
- Mux Player